Recurrent Models
- The de facto strategy in Natural Language Processing (NLP) is to encode sentences with a bidirectional LSTM models. For example: Source sentence in a translation.
- We should define our output (parse, sentence, summary) as a sequence, and use an LSTm model to generate it.
- Use of attention mechanism allows flexible access to the memory. We use attention mechanism to take a representation from our decoder and look back to treat the encoded representation as a memory, that we can reference and pick out what’s important to any given time.
Issues with Recurrent Models
- Linear interaction distance.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) are unrolled left-to-right.
- RNNs encode linear locality which means the nearby words often affect each other’s meaning in the sentence.
- RNNs take O(sequence length) steps for distant words pairs to interact which means that it is hard to learn long-distance dependencies because of the gradient problems.
- Linear order of words is sort of baked into the model because we have to unroll the RNN throughout the sequence and linear order isn’t the right way to think about sentences.
- Lack of parallelizability.
- Forward and backward passes have O(sequence length) unparallelizable operations.
- Though GPUs can perform a bunch of independent computations at once, a future RNN hidden states can’t be computed in full before past RNN hidden states have been computed.
- So, RNNs inhibits training on very large dataset.
Word Windows Model
- Word window models aggregate local context. Number of unparallelizable operations doesn’t increase sequence length.
- Stacking word window layers allows interaction between farther words.
- Maximum interaction distance = sequence length / window size. But if the sentences are too long, we will just ignore the long-distance context.
Attention Model
- Attention model treats each word’s representation as a query to access and incorporate information for a set of values. Example: In a machine translation system, the set of values were all of the encoder states for the source sentences.
- Number of unparallelizable operations doesn’t increase sequence length.
- Maximum interaction distance is O(1) since all the wrods interact at every layer.
Self-Attention Model
- Attention model operates on queries, keys, and values.
- In self-attention models, the queries, keys, and values are drawn from the same source sentences.
- Since, self-attention mechanism doesn’t build in order information, we need to encode the order of the sentences in our keys, queries, and values. We will consider representing each sequence index as a vector and add it to our inputs in *self-attention** block.
- The position representation vectors are represented through sinusoids. Sinusoidal position representations concatenate functions of varying periods. Learned absolute position representations are flexible to be learned to fit the data on each position.
Barriers & Solutions for Self-Attention Model
| Barriers | Solution |
|---|---|
| 1. Doesn’t have an inherent notion of order. | 1. Add position representations to the inputs. |
| 2. No nolinearities to produce the deep learning magic. But it’s all just the weighted averages. | 2. Apply the same feedforward networks to each self-attention output. |
| 3. Need to ensure that we don’t look at the future outputs when predicting a sequence. Like in machine translation or language modeling. | 3. Mask out the future by artificially setting the attention weights to 0. |
The necessities for a self-attention model are as follows:
- Self-attention:
- The basis of the method or implementation process.
- Position representations:
- Specify the sequence order, since self-attention is an unordered function of its inputs.
- Nonlinearities:
- At the output of the self-attention block.
- Frequently implemented as a simple feedforward network.
- Masking:
- In order to parallelize operations while not looking at the future.
- Keeps information about the future from leaking to the past.
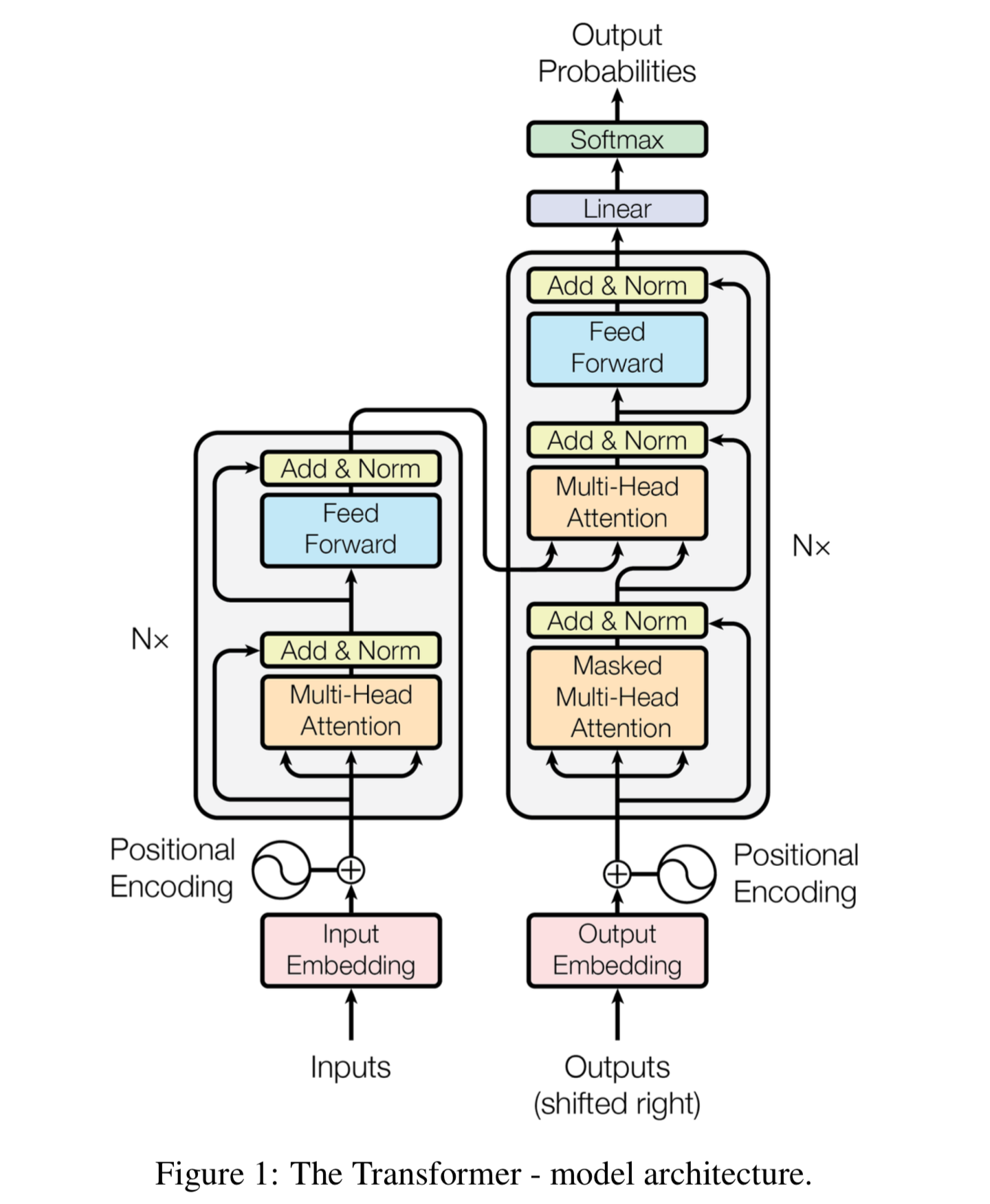
The Transformer
- We take the dot product of the query-key in one matrix multiplication.
- Then we apply softmax and compute the weighted average with another matrix multiplication.
- We define multiple attention heads through multiple query, key, and value matrices.
- Residual connections are thought to make the loss landscape considerably smoother and thus enhances easier training.
- Layer normalization is a trick to help models train faster. It cuts down on uninformative variation in hidden vector values by normalizing to unit mean and standard deviation within each layer.
- Scaled Dot Product attention is necessary when dimensionality d becomes large, dot products between vectors tend to become large and because of this, inputs to the softmax function can be large, making the gradients small.
- Transformers parallelizability allows for efficient pretraining, and have made them the de facto standard.
Word Structure and Subword Models
- In a language’s vocabulary, we assume that a fixed vocabulary of tens of thousands of words are built from the training dataset. All other novel words which are seen only at test time are mapped to a single unknown token UNK.
- Finite vocabulary assumptions in not an ideal solution in many languages. Many languages exhibit complex morphology or word structure which is more word types, each occurring in fewer times.
Byte-Pair Encoding Algorithm
Subword modeling in NLP encompasses a wide range of methods for reasoning about structure below the word level. The dominant modern paradigm is to learn a vocabulary of parts of words also known as subword tokens. At the training and testing time, each word is split into a sequence of known subwords.
Byte-pair encoding is a simple, and effective startegy for defining a subword vocabulary: - Start with a vocabulary containing only characters and an end-of-word symbol. - Using a corpus of text, find the most common adjacent characters known as subwords. - Replace instances of the character pair with the new subword and iterate until the desired vocab size is met.
This technique was originally used in NLP for machine translation, and now a similar method WordPiece is used in pretrained models.
Pretrained Word Embeddings & Models
- Almost all parameters in NLP networks are initialized via pretraining which is similar to initializing the Word2Vec parameters.
- The pretraining methods hide parts of the input from the model, and train the model to reconstruct those parts.
- This has been exceptionally effective at building strong:
- representations of language.
- parameter initializations for strong NLP models.
- probability distributions over language that we can sample from.
Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT)
- GPT is a decoder only Transformer model with 12 layers.
- GPT contains 768 dimensional hidden states, and 3072 dimensional feed-forward hidden layers.
- A subword vocabulary called Byte-Pair encoding with 40,000 merges.
- GPT models are trained on book corpus and contains over 7000 unique books which contains long spans of contiguous text, for learning long-distance dependencies.
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT)
Devlin et al., 2018 proposed the Masked LM objective and released the weights of a pretrained Transformer and labeled BERT.
Some of the details about Masked Language Model for BERT are: - Predict a random 15% of subword tokens. - Replace input word with [MASK] 80% of the time. - Replace input word with a random vocabulary token 10% of the time. - Leave input word unchanged 10% of the time but still predict.
Some of the details about BERT: - Two models were released: - BERT-base: 12 layers, 768-dim hidden states, 12 attention heads, 110 million params. - BERT-large: 24 layers, 1024-dim hidden states, 16 attention heads, 340 million params. - Trained on: - Books Corpus (800 million words) - English Wikipedia (2500 million words) - Pretraining is expensive and impractical on a single GPU: - BERT was pretrained with 64 TPU chips for a total of 4 days. - TPU are special tensor operations acceleration hardware. - Finetuning is practical and common on a single GPU.